Implant solutions
Biomaterials
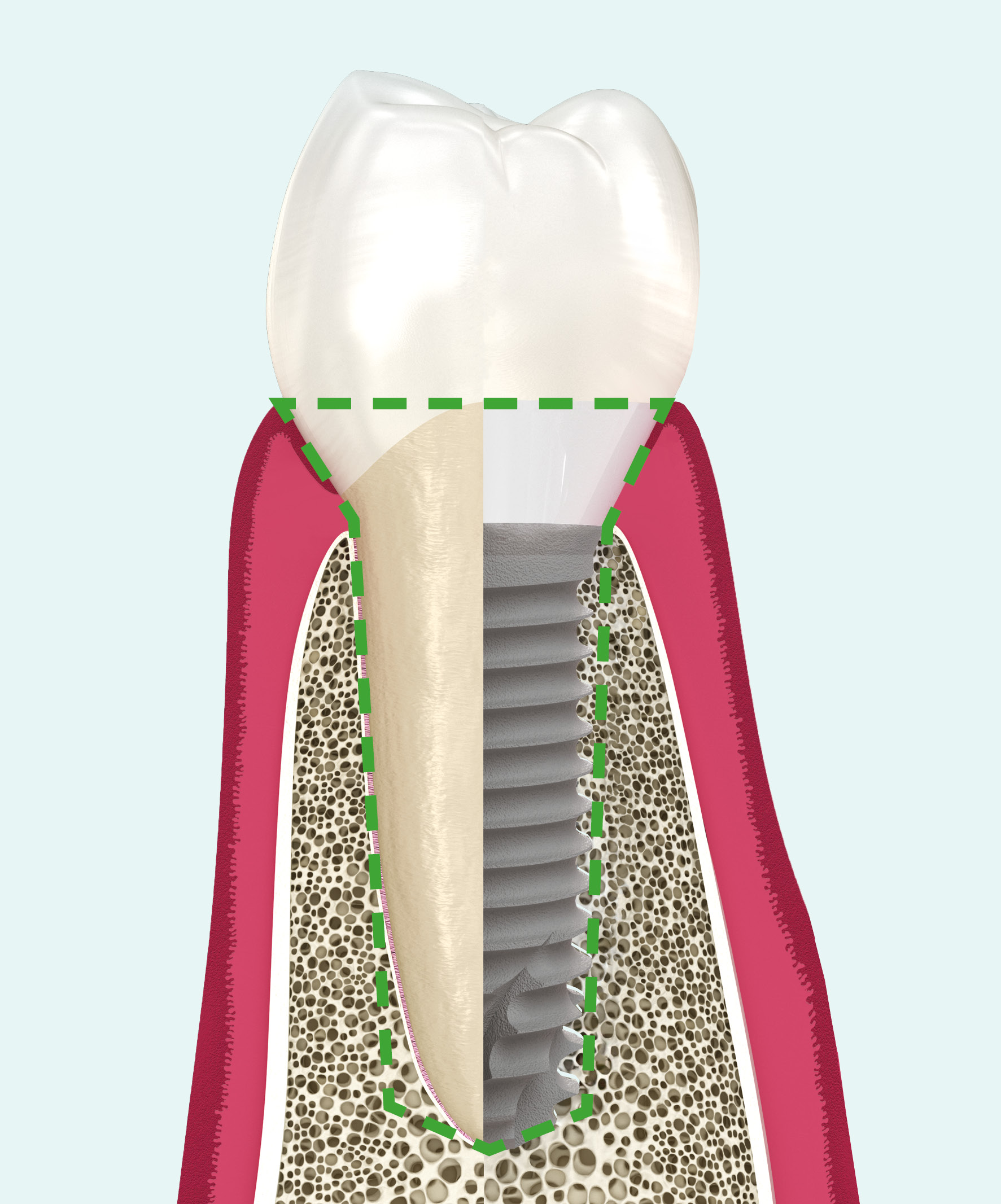
The choice of biomaterial inflfluences both osseointegration of the implant and architecture of the epithelialconnective attachment, essential for the stability and protection of peri-implant tissues.
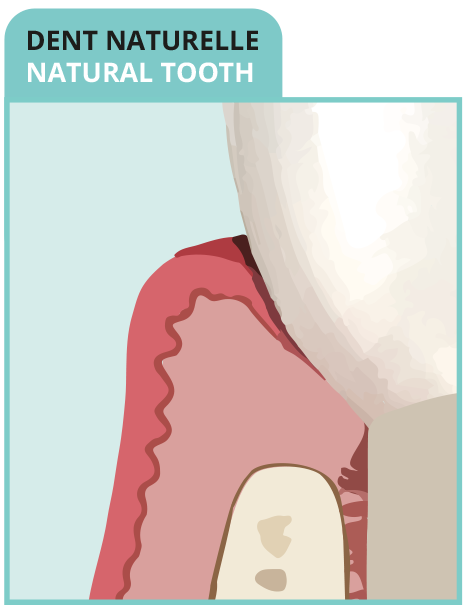
• Oblique fibers anchored in the cement
• Rich in circular fibers
• Short junctional epithelium
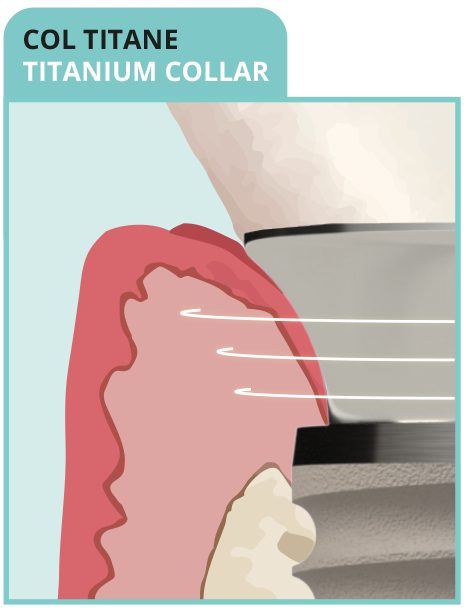
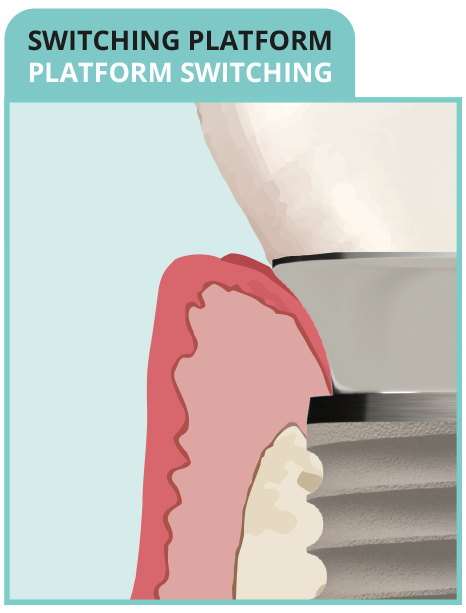
• No anchoring of collagen fibers
• Fewer circular fibers
• Long junctional epithelium + crestal bone resorption
- NON-BIOMIMETIC
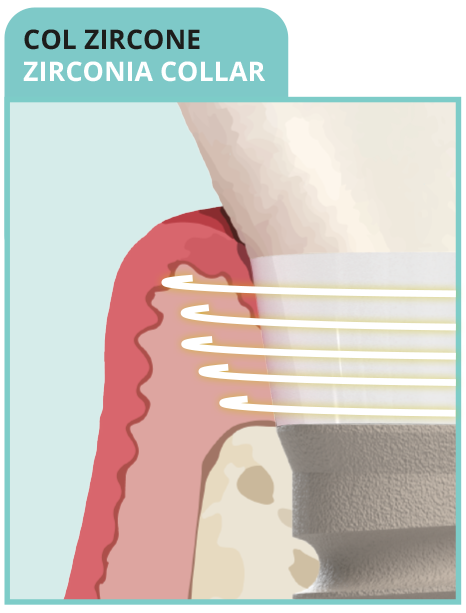
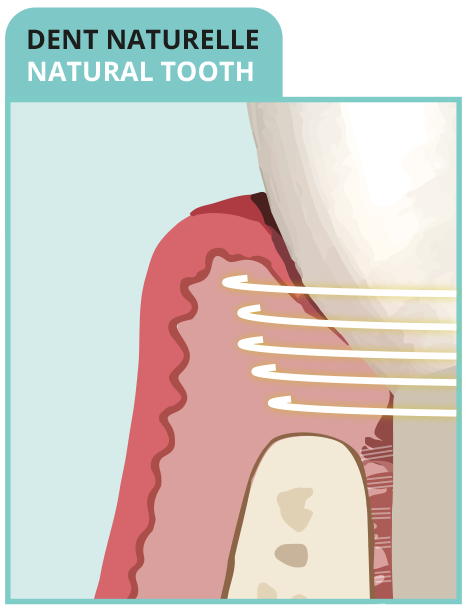
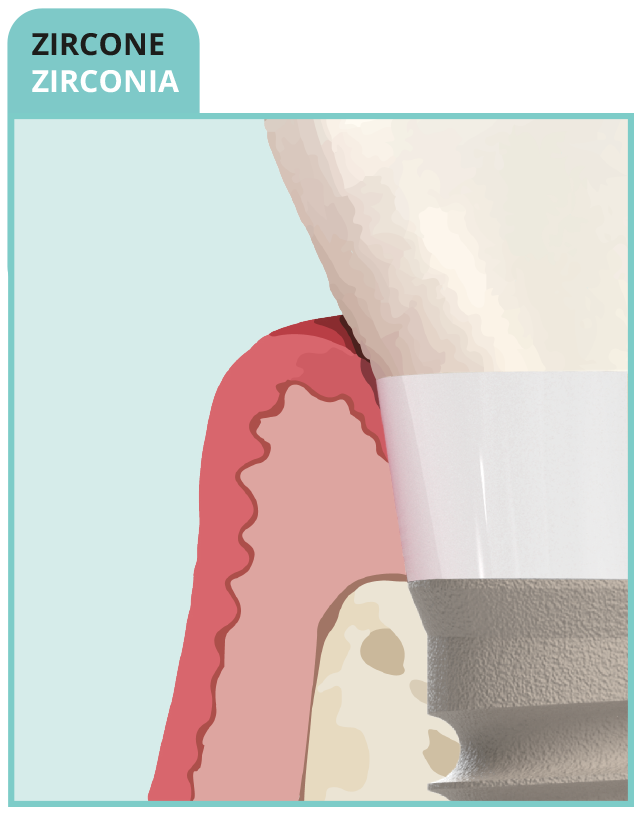
• Dense connective sleeve of collagen fibers
• Rich in circular fibers
• Short junctional epithelium
- BIOMIMETIC
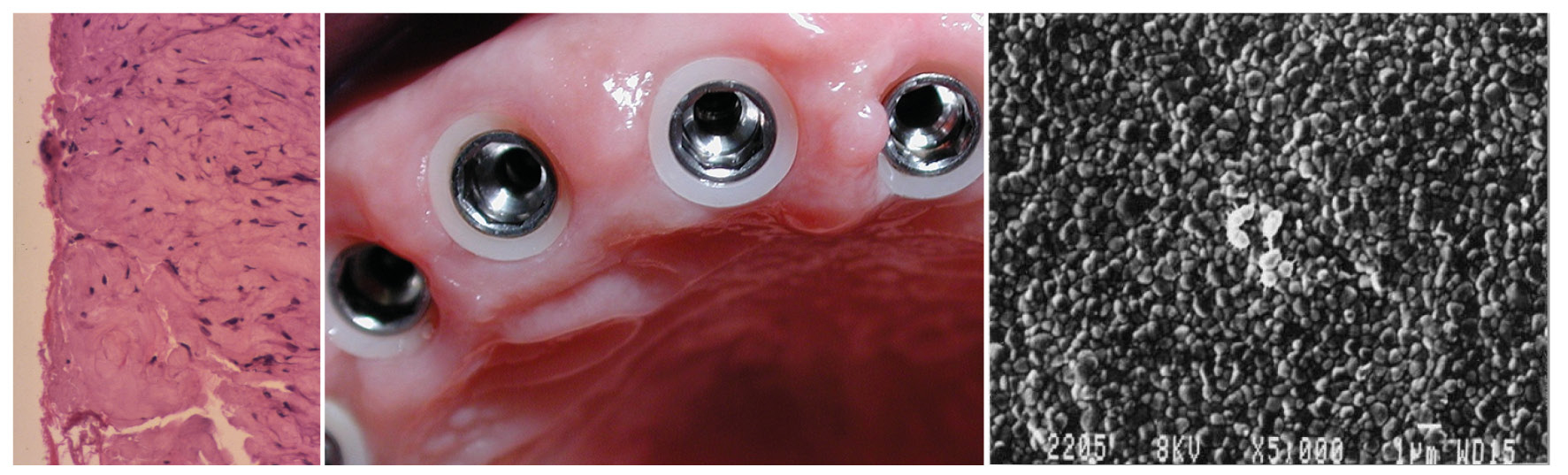
ZIRCONIA AND PERI-IMPLANT SOFT TISSUES
- Primary healing of peri-implant tissues
- Long-term gain of epithelial-connective attachment
- No cell disruption when handling prosthetic components
- Ultra-smooth surface: prevents bacterial plaque retention
- Thermal and tribocorrosion protection
- No epithelial invagination
- Short junctional epithelium with hemidesmosomes
- Underlying connective contractile sleeve, rich in circular fibers
- Stability of the biological width, without bone resorption
- Creeping coronal attachment of the gingival margin

BIOMIMETIC
inspired by natural teeth
Implant design
Various supracrestal emergence geometries are now available aiming to preserve soft-tissue health.
• Coronal emergence profile in root
extension
• Convex flare of coronal enamel
• Nautral epithelial-connective
attachment
•Emergence profile shifted and not
aligned
• Concave flare, bacterial plaque trap
• Epithelial invagination and crestal
bone loss
- NON-BIOMIMETIC
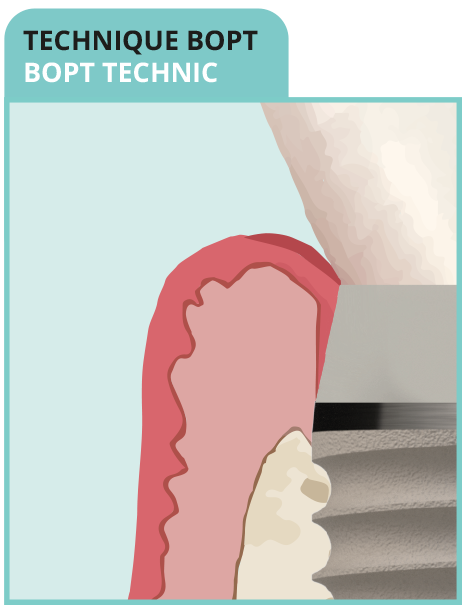
• Narrowed emergence profile reducing
the prosthetic element diameter
• Excessive coronary flare creating an
overhang
• Vulnerability of soft tissue attachment
architecture
- NON-BIOMIMETIC
- Geometry imitating the natural tooth
- Coronal emergence profile extending from the root
- Convex flaring of the zirconia collar
- Preserving biological width
- No bacterial plaque trap
- Accurate fit of the crown to the zirconia platform

BIOMIMETIC
inspired by natural teeth
Colorimetry
The translucency of titanium in transgingival applications remains a concern, and implantology manufacturers have developed industrial processes to overcome these drawbacks.

• Greyish transparency
• Grey margin in case of recession
• No impact on epithelial-connective
architecture
- NON-BIOMIMETIC
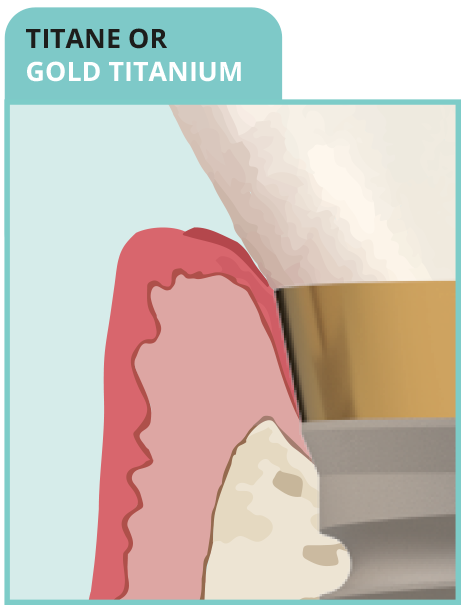
• Golden transparency
• Golden margin in case of recession
• No impact on epithelial-connective
architecture
- NON-BIOMIMETIC

• Pink transparency
• Pink margin in case of recession
• No impact on epithelial-connective
architecture
- NON-BIOMIMETIC
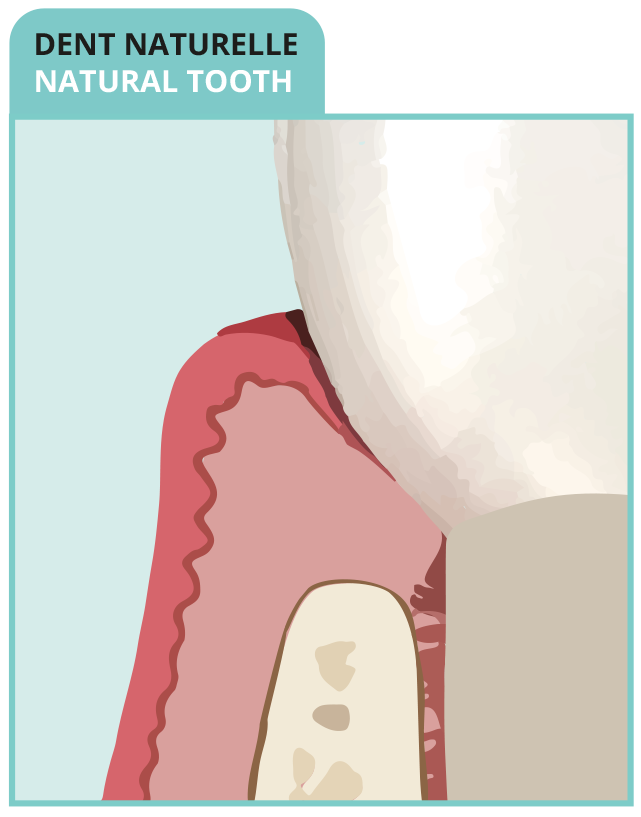
• Natural translucency of coronal enamel and dental root
• Exposure of an ivory root colour in case of gingival recession
• Original biological width
- Natural translucency of zirconia through the gum
- Exposure of an A2 shade of zirconia collar in case of gingival recession
- Preserved and functional biological width